Jupiter's primordial beat of superoutbursting stars
Jupiter’s 1996 switch to decadal global magnetodynamics of active stars unveils a new pulsar class
Article Sidebar

Vols. 1-18 (1924-1944), ISSN 0044-2801
Main Article Content
Abstract
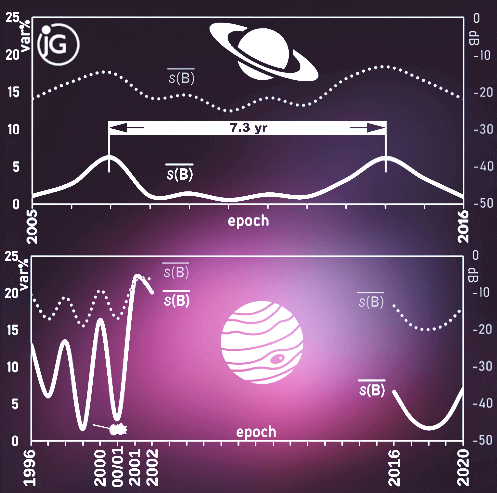
The decadal global magnetoactivity evolution profile that precedes short-burst pulses in magnetar 4U 0142+61 and superhumps (superoutbursts) in dwarf novae now also emerges from mean least-squares spectra of >12 billion mission-integrated Galileo–Cassini–Juno 1996–2020 annual samplings of Jupiter ⪅8nT global magnetic field. For the first time in any planetary magnetosphere, the profile has revealed a ubiquitous primordial physical property: the presence of a high-power, pulsar-like global dynamic from temporally mapping hyperlow-frequency (<1μHz) systematic dynamics of Jovian magnetospheric signature in the solar wind (Rieger-resonance band of 385.8–64.3 nHz or ~0.3·109–3·109 erg energetic perturbations). The signature served as a proxy of Jovian magnetoactivity expressed in mean least-squares-spectral magnitudes as a novel method for measuring relative field dynamics. The magnetoactivity impressed thus and entirely into the solar wind, and it encompassed the well-known, solar system-permeating ~154-day Rieger period and its first six harmonics. Statistical fidelity of the spectral peaks remained within a very high (Φ≫12) range of 107–105, reflecting the signature’s completeness and incessantness. The magnetoactivity upsurge from spectral means that maintained a stunning ~20% field variance (total annual energy budget) began reformatting the signature around 1999, gradually transforming it into the anomalous state by 2002, as supported by an increased anisotropic splitting of spectral peaks. By contrast, a comparison against 2005–2016 Cassini global samplings revealed a calm Saturnian magnetoactivity at a low ⪅1% field variance except for every ~7.1 yrs when it is ⪅5%, possibly due to orbital–tidal forcing. While this discovery of planetary pulsars as a new pulsar class calls for redefining pulsars to include failed stars, a global pulsation profile of the magnetar–novae type in a failed-star-turned-planet calls for beacon-orbiter missions to monitor Jupiter’s activity and its disruption capacity to solar system infrastructure. Shannon’s theory-based rigorous Gauss–Vaniček least-squares spectral analysis revolutionizes astrophysics by directly computing relative dynamics of global astrophysical fields and space physics by rigorously simulating completed orbits and fleet formations from a single spacecraft.
 ARK: https://n2t.net/ark:/88439/x001607
ARK: https://n2t.net/ark:/88439/x001607
Permalink: https://geophysicsjournal.com/article/347

Sun dims as failed star Jupiter tries to go full-on pulsar. J. Geophys. 66(1):15-24
 Read the press release for this article
Read the press release for this article
Article Details
References
Aulbach, S., Heaman, L.M., Stachel, T. (2018) The Diamondiferous Mantle Root Beneath the Central Slave Craton. Geoscience and Exploration of the Argyle, Bunder, Diavik, and Murowa Diamond Deposits. ISBN 9781629496399. https://doi.org/10.5382/SP.20.15
Bai T., Cliver E. W. (1990) A 154 day periodicity in the occurrence rate of proton flares. Astrophys. J. 363:299–309. https://doi.org/10.1086/169342
Cane, H.V., Richardson, I.G., von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1998) Interplanetary magnetic field periodicity of ∼153 days. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25(24):4437–4440. https://doi.org/10.1029/1998GL900208
Carbonell, M., Ballester, J.L. (1992) The periodic behaviour of solar activity – The near 155-day periodicity in sunspot areas. Astron. Astrophys. 255(1–2):350–362. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/#abs/1992A&A...255..350C
Chancia, R.O., Hedman, M.M., Cowley, S.W.H., Provan, G., Ye, S.–Y. (2019) Seasonal structures in Saturn's dusty Roche Division correspond to periodicities of the planet's magnetosphere. Icarus 330:230–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2019.04.012
Chapman, S.C., Watkins, N.W., Dendy, R.O., Helander, P., Rowlands, G. (1998) A simple avalanche model as an analogue for magnetospheric activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25(13):2397-2400. https://doi.org/10.1029/98GL51700
Chauvin, G., Lagrange, A.–M., Zuckerman, B., Dumas, C., Mouillet, D., et al. (2005) A companion to AB Pic at the planet/brown dwarf boundary. Astron. Astrophys. 438(3):L29–L32. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:200500111
Cho, J.–H., Lee, D.–Y., Noh, S.–J., Kim, H., Choi, C.R., et al. (2017) Spatial dependence of electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves triggered by solar wind dynamic pressure enhancements. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 122, 5502–5518. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JA023827
Chowdhury, P., Khan, M., Ray, P.C. (2009) Intermediate-term periodicities in sunspot areas during solar cycles 22 and 23. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 392(1):1159–1180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14117.x
Craymer, M.R. (1998) The Least Squares Spectrum, Its Inverse Transform and Autocorrelation Function: Theory and Some Applications in Geodesy. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, Canada. https://hdl.handle.net/1807/12263
Dessler, A.J. (1987) Magnetospheric power from planetary spin (p.71). IEEE international conference on plasma science, 1–3 June, Crystal City, VA USA
Dib, R., Kaspi, V.M., Gavriil, F.P. (2007) 10 Years of RXTE monitoring of the anomalous X-ray pulsar 4U 0142+61: long-term variability. Astrophys. J. 666(2):1152-1164. https://doi.org/10.1086/519726
Dimitropoulou, M., Moussas, X., Strintzi, D. (2008) Enhanced Rieger type periodicities' detection in X-ray solar flares and statistical validation of Rossby waves' existence. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 4(S257):159–163. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1743921309029226
Dougherty, M.K., Kellock, S., Slootweg, A.P., Achilleos, N., Joy, S.P., Mafi, J.N. (2006) Cassini orbiter magnetometer calibrated 1 minute averaged archive v2.0 & v.1.0, CO-E/SW/J/S-MAG-4-SUMM-AVG1MIN-V2.0. NASA Planetary Data System. https://doi.org/10.17189/1519602
Dowden, R.L. (1968) A Jupiter Model of Pulsars. Pubs. Astron. Soc. Austral. 1(4):159–159. https://doi.org/10.1017/s132335800001122x
Duarte, L.D.V., Wicht, J., Gastinec, T. (2018) Physical conditions for Jupiter-like dynamo models. Icarus 299:206–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2017.07.016
Fan, C.Y., Wu, J., Hang, H. (1982) Scaling from Jupiter to pulsars and mass spectrum of pulsars. Astrophys. J. 260(1):353–361. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1982ApJ...260..353F
Fukuhara, M. (2020) Possible nuclear fusion of deuteron in the cores of Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, and brown dwarfs. AIP Advances 10:035126. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5108922
García, C.R., Torres, D.F. (2023) Quantitative determination of minimum spanning tree structures: using the pulsar tree for analysing the appearance of new classes of pulsars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 520(1):599–610. https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stad183
Gaulme, P., Schmider, F.-X., Gay, J., Guillot, T., Jacob, C. (2011) Detection of Jovian seismic waves: a new probe of its interior structure. Astron. Astrophys. 531:A104. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201116903
Ge, Y.S., Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T. (2007) Growth phase of Jovian substorms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34:L23106. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL031987
Gonzalez, M.E., Dib, R., Kaspi, V.M., et al. (2010) Long-term X-ray changes in the emission from the anomalous X-ray pulsar 4U 0142+61. Astrophys. J. 716:1345–1355. https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/716/2/1345
Grote, E., Busse, F.H. (2000) Hemispherical dynamos generated by convection in rotating spherical shells. Phys. Rev. E 62:4457–4460. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.62.4457
Kinkhabwala, A. (2013) Maximum Fidelity. Max Planck Institute of Molecular Physiology report. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1301.5186
Kiplinger, A.L., Dennis, B.R., Orwig, L.E. (1984) Detection of a 158 Day Periodicity in the Solar Hard X-Ray Flare Rate. Bull. Amer. Astron. Soc. 16:891. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/#abs/1984BAAS...16..891K
Kuznetsova, Yu.G., Pavlenko, E.P., Sharipova, L.M., Shugarov, S.Yu. (1999) Observations of Typical, Rare and Unique Phenomena in Close Binaries with Extremal Mass Ratio. Odessa Astron. Pub. 12:197–200. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/#abs/1999OAP....12..197K
Lou, Y.–Q., Wang, Y.–M., Fan, Z., Wang, S., Wang, J.X. (2003) Periodicities in solar coronal mass ejections. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 345(3):809–818. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-8711.2003.06993.x
Luhman, K.L., Adame, L., D'Alessio, P., Calvet, N., Hartmann, L., et al. (2005) Discovery of a planetary-mass brown dwarf with a circumstellar disk. Astrophys. J. 635(1):L93. https://doi.org/10.1086/498868
Manners, H., Masters, A. (2020) The global distribution of ultralow-frequency waves in Jupiter's magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 125:e2020JA028345. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JA028345
Masters, M. (2017) Revealing how the solar wind interacts with Jupiter’s magnetosphere. Magnetospheres of the outer planets (MOP), Conference by the Swedish Institute for Space Physics and Royal Institute of Technology, Uppsala Sweden, 12–16 June.
Matsushita, S. (1967) Solar quiet and lunar daily variation fields. In: Matsushita S. Campbell W.H. (Eds.) Physics of Geomagnetic Phenomena: International Geophysics Series, Vol. 2, p. 301–424. Academic Press Inc., New York. Reprint 2016, Elsevier. ISBN 9781483222523. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-480301-5.50013-6
Michel, F.C. (1982) Theory of pulsar magnetospheres. Rev. Mod. Phys. 54:1. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.54.1
Moore, K.M., Yadav, R.K., Kulowski, L., Cao, H., Bloxham, J., et al. (2018) A complex dynamo inferred from the hemispheric dichotomy of Jupiter’s magnetic field. Nature 561:76–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0468-5
Murakami, G., Yoshioka, K., Yamazaki, A., Tsuchiya, F., Kimura, T., et al. (2016) Response of Jupiter's inner magnetosphere to the solar wind derived from extreme ultraviolet monitoring of the Io plasma torus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43:12308–12316. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL071675
von Neumann, J. (1941) Distribution of the Ratio of the Mean Square Successive Difference to the Variance. Ann. Math. Statist. 12(4):367–395. https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177731677
Omerbashich, M. (2024) Sun dims as failed star Jupiter tries to go full-on pulsar. J. Geophys. 66(1):15–24. https://n2t.net/ark:/88439/x010002
Omerbashich, M. (2023a) The Sun as a revolving-field magnetic alternator with a wobbling-core rotator from real data. J. Geophys. 65(1):48-77. https://n2t.net/ark:/88439/x080008
Omerbashich, M. (2023b) Global coupling mechanism of Sun resonant forcing of Mars, Moon, and Earth seismicity. J. Geophys. 65(1):1–46. https://n2t.net/ark:/88439/x040901
Omerbashich, M. (2023c) Earth as a time crystal: macroscopic nature of a quantum-scale phenomenon exposes quantum physics as tidally-resonantly localized to host star. arXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.02578
Omerbashich, M. (2021) Non-marine tetrapod extinctions solve extinction periodicity mystery. Hist. Biol. 34(1):188-191. https://doi.org/10.1080/08912963.2021.1907367
Omerbashich, M. (2020) Moon body resonance. J. Geophys. 63:30–42. https://n2t.net//88439/x034508
Omerbashich, M. (2009) Method for Measuring Field Dynamics. US Patent #20090192741, US Patent & Trademark Office. https://worldwide.espacenet.com/publicationDetails/biblio?CC=US&NR=2009192741A1
Omerbashich, M. (2007) Magnification of mantle resonance as a cause of tectonics. Geodinamica Acta 20:6:369–383. https://doi.org/10.3166/ga.20.369-383
Omerbashich, M. (2006) Gauss–Vaníček Spectral Analysis of the Sepkoski Compendium: No New Life Cycles. Comp. Sci. Eng. 8(4):26–30. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCSE.2006.68 (Erratum due to journal error. Comp. Sci. Eng. 9(4):5–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCSE.2007.79;
full text at: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.math-ph/0608014)
Omerbashich, M. (2004) Earth-model Discrimination Method. Ph.D. Dissertation, pp.129. ProQuest, USA. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.12847304
Pagiatakis, S. (1999) Stochastic significance of peaks in the least-squares spectrum. J. Geod. 73:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900050220
Pap, J., Tobiska, W.K., Bouwer, S.D. (1990) Periodicities of solar irradiance and solar activity indices, I. Sol. Phys. 129:165–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00154372
Pizzocaro, D., Tiengo, A., Mereghetti, S., Turolla, R., Esposito, P., et al. (2019) Detailed X-ray spectroscopy of the magnetar 1E 2259+586. Astron. Astrophys. 626:A39. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201834784
Press, W.H., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T., Flannery, B.P. (2007) Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing (3rd Ed.). Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom. ISBN 9780521880688
Rieger, E., Share, G.H., Forrest, D.J., Kanbach, G., Reppin, C., et al. (1984) A 154-day periodicity in the occurrence of hard solar flares? Nature 312:623–625. https://doi.org/10.1038/312623a0
Roussos, E., Krupp, N., Paranicas, C., Kollmann, P., Mitchell, D.G., et al. (2018) Heliospheric conditions at Saturn during Cassini's ring-grazing and proximal orbits. Geophys. Res. Lett. 45:10812–10818. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL078093
Rubenstein, E.P., Schaefer, B.E. (2000) Are Superflares on Solar Analogues Caused by Extrasolar Planets? Astrophys. J. 529(2):1031. https://doi.org/10.1086/308326
Saur, J., Schreiner, A., Mauk, B.H., Clark, G.B., Kollmann, P. (2017) Wave particle interactions in Jupiter’s magnetosphere and associated particle acceleration. Magnetospheres of the outer planets (MOP), Conference by the Swedish Institute for Space Physics and Royal Institute of Technology, Uppsala Sweden, 12–16 June.
Schaefer, B.E., King, J.R., Deliyannis, C.P. (2000) Superflares on ordinary solar-type stars. Astrophys. J. 529(2):1026. https://doi.org/10.1086/308325
Shannon, C.E. (1948) A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell System Tech. J. 27:379–423, 623–656. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x
Sheppard, S.S., Tholen, D.J., Alexandersen, M., Trujillo, C.A. (2023) New Jupiter and Saturn Satellites Reveal New Moon Dynamical Families. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 7(5):100. https://doi.org/10.3847/2515-5172/acd766
Spruit, H.C. (2017) Essential magnetohydrodynamics for astrophysics. An introduction to magnetohydrodynamics in astrophysics. Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics report. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1301.5572
Stallard, T.S., Baines, K.H., Melin, H., Bradley, T.J., Moore, L., et al. (2019) Local-time averaged maps of H3+ emission, temperature and ion winds. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 3772018040520180405. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2018.0405
Steeves, R.R. (1981). A statistical test for significance of peaks in the least squares spectrum. Collected Papers, Geodetic Survey, Dept. of Energy, Mines and Resources. Surveys and Mapping Branch, Ottawa Canada, pp. 149–166. http://www2.unb.ca/gge/Research/GRL/LSSA/Literature/Steeves1981.pdf
Taylor, J., Hamilton, S. (1972) Some tests of the Vaníček Method of spectral analysis. Astrophys. Space Sci. 17:357. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00642907
Tsuchiya, F., Yoshioka, K., Kimura, T., Koga, R., Murakami, G., et al. (2018) Enhancement of the Jovian magnetospheric plasma circulation caused by the change in plasma supply from the satellite Io. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 123:6514–6532. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JA025316
Vaníček, P. (1969) Approximate spectral analysis by least-squares fit. Astrophys. Space Sci. 4(4):387–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00651344
Vaníček, P. (1971) Further development and properties of the spectral analysis by least-squares fit. Astrophys. Space Sci. 12(1):10–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00656134
Vogt, M.F., Gyalay, S., Kronberg, E.A., Bunce, E.J., Kurth, W.S., et al. (2019) Solar wind interaction with Jupiter’s magnetosphere: a statistical study of Galileo in situ data and modeled upstream solar wind conditions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 124(12):10170–10199. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JA026950
Wells, D.E., Vaníček, P., Pagiatakis, S. (1985) Least squares spectral analysis revisited. Dept. of Geodesy & Geomatics Engineering, Technical Report 84, U. of New Brunswick, Canada. http://www2.unb.ca/gge/Pubs/TR84.pdf
de Wit, J., Lewis, N.K., Knutson, H.A., Fuller, J., Antoci, V., et al. (2017) Planet-induced Stellar Pulsations in HAT-P-2's Eccentric System. Astrophys. J. Lett. 836(2):L17. https://doi.org/10.3847/2041-8213/836/2/L17
Woods, P.M., Kaspi, V.M., Thompson, C., Gavriil, F.P., et al. (2004) Changes in the X-Ray emission from the magnetar candidate 1E 2259+586 during its 2002 outburst. Astrophys. J. 605(1):378-399. https://doi.org/10.1086/382233
Wright, A.N., Mann, I.R. (2013) Global MHD eigenmodes of the outer magnetosphere. In: Magnetospheric ULF Waves: Synthesis and New Directions. Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 169:51–72. https://doi.org/10.1029/169GM06
Yao, Z., Dunn, W.R., Woodfield, E.E., Clark, G., Mauk, B.H., et al. (2021) Revealing the source of Jupiter’s x-ray auroral flares. Sci. Adv. 7:eabf0851. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abf0851
Zhou, W.X., Sornette, D. (2002) Statistical significance of periodicity and log-periodicity with heavy-tailed correlated noise. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 13(2):137-169. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129183102003024